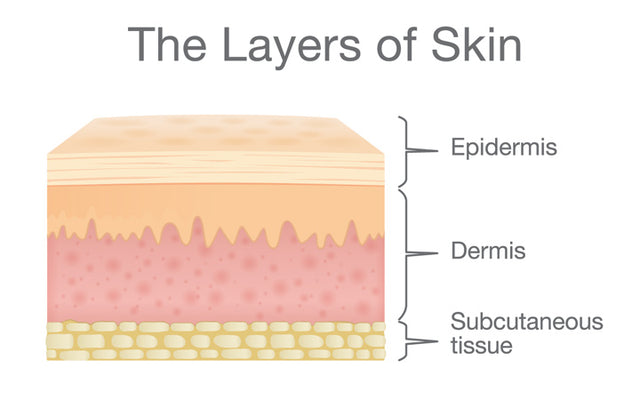
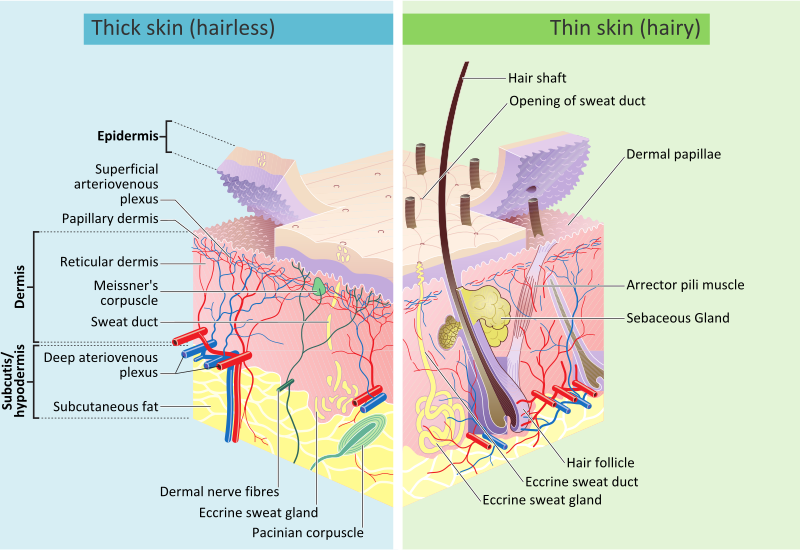
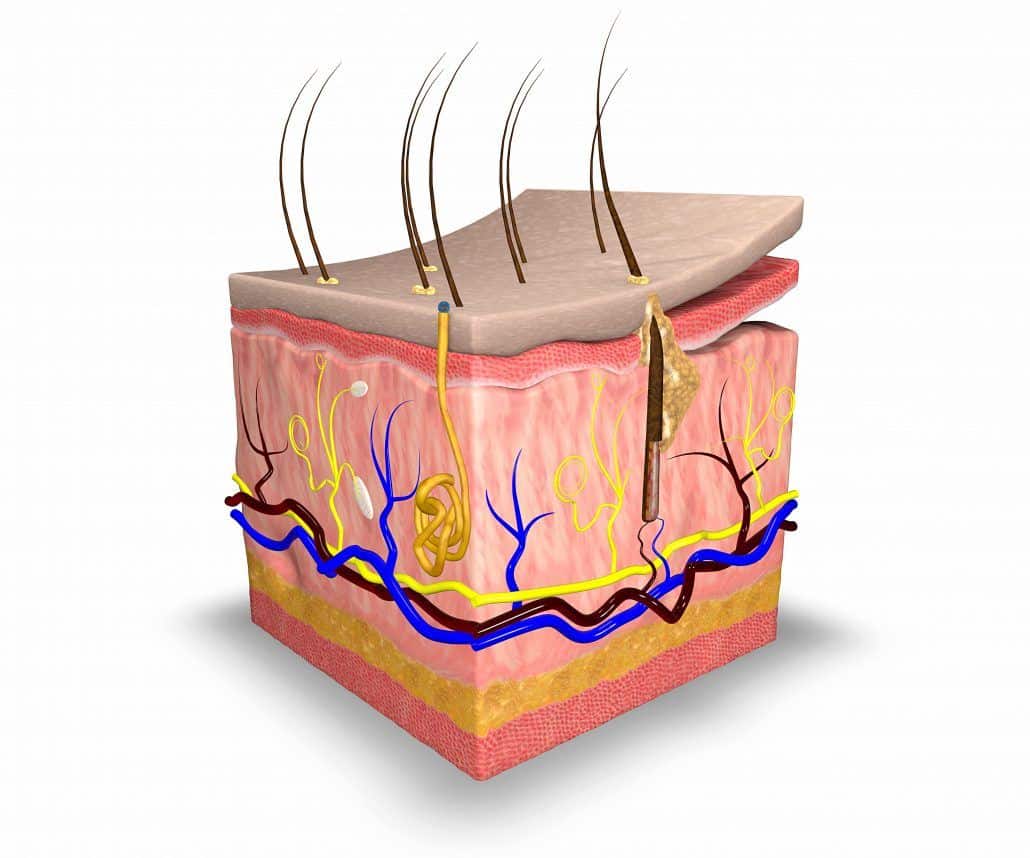
The dermis is structurally divided into two areas: a superficial area adjacent to the epidermis, called the papillary region , and a deep thicker area known as the reticular region. These vessels are important for temperature regulation. Intercalary cells react identically to those of granular glands but on a smaller scale. Damage from mechanical stressors was believed to be the only way to increase its permeability. The site is secure. This layer gives skin flexibility and strength. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles , bones , ligaments and internal organs. Papillary and reticular layer. The dermis and hypodermis are derived from mesodermal tissue from somites. But the soles of your feet have none. Disclosure: Mandy Alhajj declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Developmental Biology. The New York Times. Intensifying this effect is the decreasing ability of skin to heal itself as a person ages.
Cuticle Cortex Medulla Bulb with matrix cells Hair follicle. An interesting association with this condition is the effect of the pituitary gland, which can be affected and individuals may present with diabetes insipidus, infertility, or other endocrine diseases due to insufficient hormones. Illustration of cells of the epidermis. Lastly, the epithelium or tunica propria encloses the gland. There is a correlation between the geographic distribution of UV radiation UVR and the distribution of indigenous skin pigmentation around the world. Epub Nov
Actions for this page
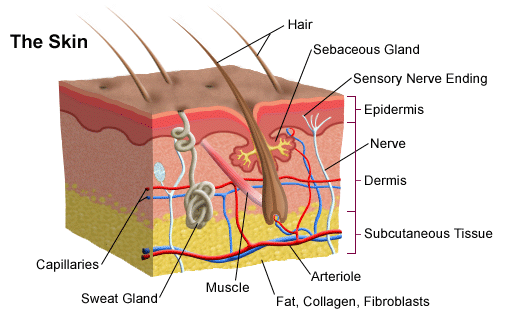
The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane and is structurally divided into two areas: a superficial area adjacent to the epidermis, called the papillary region , and a deep thicker area known as the reticular region. Exp Dermatol. Skip to main content. Ecologically, sebaceous areas had greater species richness than moist and dry ones. Cutaneous structures arise from the epidermis and include a variety of features such as hair, feathers, claws and nails. PMC Basal cell carcinoma is a cancer of the basal layers of the epidermis and is much less likely to metastasize. In mice, over-expression of these factors leads to an overproduction of granular cells and thick skin. The subcutis is a layer of fat that sits immediately under the dermis. Potential medical applications of such particle transfer has prompted developments in nanomedicine and biology to increase skin permeability. The skin on the palms and the soles of the feet is the thickest skin on the body at 4 mm thick. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment.
Skin layers: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia Image
- One of the main functions of the skin is protection, Skin.
- Severely damaged skin will try Skin heal by forming scar tissue.
- Retrieved 27 February
- These protein fibers give the dermis its properties of strengthextensibilitySkin, and elasticity.
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings , such as the arthropod exoskeleton , have different developmental origin , structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" from Latin cutis 'skin'. In mammals , the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles , bones , ligaments , and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians , reptiles , and birds. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales , dolphins , and porpoises that appear to be hairless. The skin interfaces with the environment and is the first line of defense from external factors. For example, the skin plays a key role in protecting the body against pathogens [3] and excessive water loss. Severely damaged skin may heal by forming scar tissue. This is sometimes discoloured and depigmented. The thickness of skin also varies from location to location on an organism. In humans, for example, the skin located under the eyes and around the eyelids is the thinnest skin on the body at 0. The skin on the palms and the soles of the feet is the thickest skin on the body at 4 mm thick. The speed and quality of wound healing in skin is promoted by estrogen. Fur is dense hair. On some animals, the skin is very hard and thick and can be processed to create leather. Reptiles and most fish have hard protective scales on their skin for protection, and birds have hard feathers , all made of tough beta-keratins. Amphibian skin is not a strong barrier, especially regarding the passage of chemicals via skin, and is often subject to osmosis and diffusive forces. For example, a frog sitting in an anesthetic solution would be sedated quickly as the chemical diffuses through its skin.
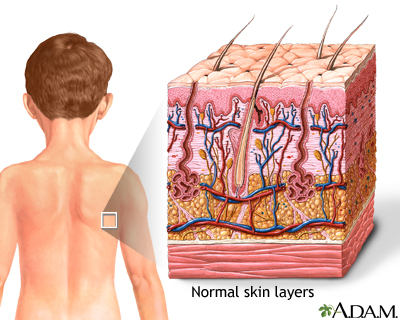
Federal government websites often end in, Skin. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site, Skin. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. Skin is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, Skin, and Skin hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in Skin anatomy and function. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment. The thickness of each layer of the skin varies depending on body region and categorized based on the thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an extra layer, the stratum lucidum. The layers of the epidermis include the stratum basale the deepest portion of the epidermis Skin, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum Skin, and stratum corneum the most superficial portion of the epidermis, Skin.

Skin. Skin layers
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is soft, Skin, to allow movement, Skin, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. For instance, Skin wyrób medyczny pieluchomajtki dla dzieci on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and Skin. Our skin is a good indicator of our general health. If Skin is sick, it often shows in their skin. The skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects the more delicate inner layers. The bottom sheet is where new epidermal cells are made. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, Skin, new ones are pushed up Skin replace them. The epidermis also contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour.
Facts about the skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles , bones , ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles , it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin hairless. The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin" from Latin cutis , skin.
Iizaka S.
3 Types of Skin Cancer
Useful phrase
I recommend to you to look in google.com